Vibe Coding Basics: Usage, Sessions, Permissions, and Model Selection

This article covers the basic concepts and settings of vibe coding tools. It summarizes essential knowledge common to Claude Code and Codex, including usage management, session concepts, context and compact, file permissions, web search, and model selection.
To make the most of vibe coding tools, you need to understand some basic concepts and configure settings. Claude Code and Codex share similar structures, so once you learn one, you can easily adapt to any tool.
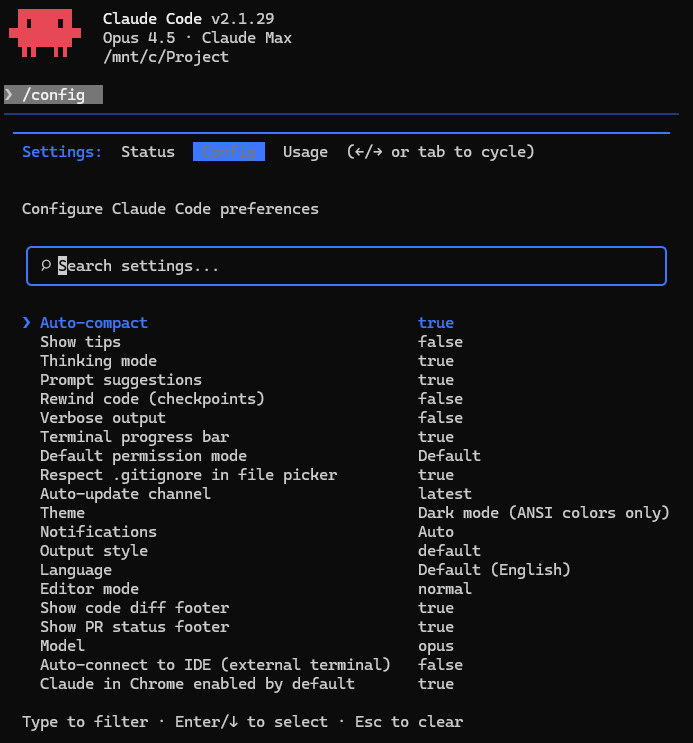
Settings file locations:• Claude Code: ~/.claude/settings.json
• Codex: ~/.codex/config.toml
• /config command to open settings screen (common)
Once you've completed installation, you can now proceed with help from the coding agent. Rather than manually editing settings files, it's recommended to ask the agent things like "turn on web search" or "change the default model to Opus." You don't need to memorize file paths or syntax—the agent handles it for you.
Usage and Pricing
Most vibe coding tools operate on subscription-based pricing. Free trials are available, but paid subscriptions are required for serious work.
Claude Code:• Requires Anthropic's Claude Pro/Max subscription ($20/month ~)
• Weekly usage limits apply. High-performance models like Opus deplete faster
• When usage is exhausted, wait until next week or switch to cheaper models (Haiku)
• Check usage: /status command in CLI, status bar or settings panel in IDE/desktop app
Codex:• Requires OpenAI's ChatGPT Plus/Pro subscription ($20/month ~)
• Similarly has weekly/monthly usage limits
• Pro subscription provides higher usage limits
• Check usage: /status in CLI, UI in IDE/desktop
To manage usage efficiently, use cheaper models for simple tasks and high-performance models only for complex work. Reducing unnecessary conversation and giving clear instructions at once helps save usage.
Project Root Settings
Before running vibe coding tools, you need to specify the project folder to work with. The tool reads files, makes modifications, and executes commands based on this folder.
Setting in CLI:Navigate to the project folder in terminal before running.
``bash``
cd ~/my-project
claude # or codex
Setting in Desktop/IDE:• Claude Desktop: Select folder using 'Select folder' button in Code tab
• VS Code extension: Currently open workspace automatically becomes project root
If you set the wrong project root, you might modify wrong files or fail to find necessary files. Always verify you're starting from the correct folder before working.
Permissions
You need to configure permissions for vibe coding tools to read and write files. By default, access is restricted to files within the project directory, but you can adjust as needed.
Permission types:• Read permission: Permission to read files for code analysis, search, and understanding
• Write permission: Permission to create new files and modify existing ones
• Execute permission: Permission to run terminal commands (build, test, etc.)
Configuration methods:• Claude Code: Configure detailed permissions with allow, deny, ask arrays in ~/.claude/settings.json or project's .claude/settings.json. Example: specify patterns like Bash(npm run *), Read(./.env)
• Codex: Select mode with --sandbox flag. Choose from workspace-write (default), read-only, danger-full-access. Use --yolo flag to skip all approvals
It's safe to start in 'cautious mode' requesting confirmation for all actions. As you become familiar with the tool, you can set trusted actions to auto-approve for faster workflow. However, dangerous operations like git push or file deletion should always require confirmation.
Web Search
AI model training data has time limitations. Latest library documentation, new API changes, and recently released tool usage need to be found in real-time through web search.
With web search enabled:
• Access latest official documentation
• Check breaking changes in new versions
• Search community solutions on Stack Overflow, etc.
• Check latest security vulnerability information
Configuration methods:• Claude Code: Enabled by default. Automatically performs web search when needed
• Codex: Disabled by default. Enable with codex --search flag or add web_search_request = true in ~/.codex/config.toml
However, web search can increase response time and add costs. It's efficient to turn it off for tasks where basic knowledge suffices and only enable when latest information is needed.
Model Selection
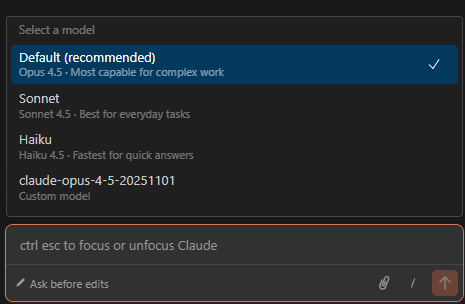
Select the AI model to use. Performance, speed, and cost vary by model, so choose according to task requirements.
Claude Code models (as of February 2026):• Opus 4.5: Top-tier model. Suitable for complex architecture design, large-scale refactoring, difficult bug fixes. Slow but highly accurate.
• Sonnet 4: Default model. Optimized for general coding tasks with good balance of speed and quality. Recommended for most tasks.
• Haiku: Lightweight model. Use for simple tasks or when fast responses are needed. Cost-effective.
Codex models (as of February 2026):• codex-max-5.2: Default model. Excellent code generation quality with coding-specialized training.
• GPT-5.2: General-purpose model, but many users prefer it for complex problems requiring deep thinking.
• Reasoning Effort: Adjusts reasoning intensity separately from model. Choose from Low/Medium/High/xHigh—higher means deeper thinking but slower responses.
Configuration methods:• /model command to change model (common)
• Claude Code: Can also specify with --model opus flag when running CLI
• Codex: Adjust Reasoning Effort in settings menu
It's efficient to start with default models (Sonnet 4, codex-max-5.2) and switch to higher models or higher reasoning effort when encountering complex problems.
Session Concept
In vibe coding, a 'session' means one continuous conversation flow. Within a session, the AI remembers previous conversation content and maintains context.
Session characteristics:• Within the same session, you can reference context like "that file earlier" or "the function we just created"
• Starting a new session erases previous conversation content (blank slate)
• Long sessions reach context limits
Session management commands:• /new: End current session and start new one (resets conversation)
• /resume: Reload previous session to continue work
When to start a new session?
• When starting completely different work
• When you want to discard incorrect context from previous conversation
• When context becomes too complex and AI gets confused
It's efficient to keep related work like implementing a feature or fixing a bug in the same session.
Context and Compact
AI models have limits on how much text they can process at once. This is called the 'context window.' As conversations grow longer, you reach this limit—this is when 'compact' summarizes and compresses previous conversation.
When compact happens:• AI remembers previous conversation as summary
• Detailed content (specific code lines, exact expressions, etc.) may be lost
• Core context and decisions are retained
Compact commands and settings:• /compact: Manually summarize current conversation to free up context (CLI, IDE, desktop common)
• Auto-compact: Automatically compresses when context reaches threshold (~75%). Enabled by default in both Claude Code and Codex
However, compact can lose important context during summarization and is still unstable. Unless unavoidable, starting a new session with /new is more reliable.
Conclusion
We've covered the basic concepts and settings of vibe coding tools. Once you learn usage management, permission settings, web search, model selection, session concepts, and context/compact, you can quickly adapt to any tool whether it's Claude Code or Codex. Next, learn about project-specific settings (CLAUDE.md, codex.md).